Moneide Chemicals
Tel: 86-315-8309571
WhatsApp/WeChat/Mobile: 0086-15633399667
Skype: janet-honest
Mail: sales@moneidechem.com
Address: 2-7-523 Jidong Building Materials Tangshan, Hebei 064000 China
|
Chemical Name |
SudanⅠ |
|
CAS No. |
842-07-9 |
|
Molecular formula |
C16H12N2O |
|
EINECS No. |
212-668-2 |
|
Molecular weight |
248.28 |
|
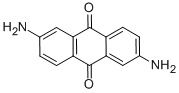
Molecular Structure |
|
|
Details |
Appearance: Wine powder Biological stain: Passes test Solubility in alcohol: Passes test Melting point: 129~134℃ Sulfated ash: 0.6% max Loss on drying: 4.0% max Solubility: insolve in water and lye, solve in aether, benzene and carbon bisulfide, solving in vitriol takes on carmine. Packing: 25kg/ fibre drum |
|
Main Application |
Used as biological dyeing agents, such as the coloring of lipoidsubstance in biological tissue; Oil coloring. |
1. What is Sudan 1?
Sudan 1 is a synthetic azo dye (chemical name: 1-phenylazo-2-naphthol) characterized by its bright red-orange color. Classified as a lipophilic (fat-soluble) compound, it belongs to the Sudan dye family, which includes Sudan II, III, and IV. Initially developed for industrial applications, Sudan 1 is now strictly regulated due to its potential carcinogenicity. It appears as a crystalline powder and dissolves readily in organic solvents like ethanol or acetone but not in water. Its use in food products is banned globally, though it persists in limited industrial and laboratory contexts.
2. What is Sudan 1 used for?
Historically, Sudan 1 was employed as a colorant for oils, waxes, and plastics, as well as in shoe and floor polishes. In laboratories, it serves as a biological stain to identify lipids in tissues during microscopy. Despite its effectiveness, its primary notoriety stems from past misuse as an illegal adulterant in food products (e.g., chili powder) to enhance color. Today, its applications are restricted to non-edible industrial uses, such as dyeing solvents and fuels, with strict handling protocols to minimize health risks.
3. What is the Sudan I stain for?
The Sudan I stain is primarily used in histology and pathology to detect and visualize lipids, triglycerides, and lipoproteins in tissue samples. When applied, it binds to fat droplets, staining them bright orange-red under a microscope. This makes it valuable for diagnosing metabolic disorders or studying adipose tissue. However, due to toxicity concerns, many labs now prefer safer alternatives like Sudan IV or Oil Red O. Its role persists in educational demonstrations and specialized research where its distinct color contrast remains advantageous.