Moneide Chemicals
Tel: 86-315-8309571
WhatsApp/WeChat/Mobile: 0086-15633399667
Skype: janet-honest
Mail: sales@moneidechem.com
Address: 2-7-523 Jidong Building Materials Tangshan, Hebei 064000 China
Fluorexon
|
Chemical Name |
Fluorexon |
|
Another name |
Fluorescein di-(methylimino diacetic acid); Fluorescein Complexon; Bis[N,N-bis(carboxymethyl)aminomethyl]fluorescein; Calcein |
|
CAS No. |
1461-15-0 |
|
Molecular formula |
C30H26N2O13 |
|
EINECS No. |
215-957-1 |
|
Molecular weight |
622.53 |
|
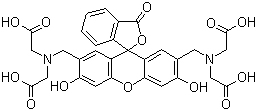
Molecular Structure |
|
|
Details |
Appearance: orange powder Water Soluble Test: pass Sensitivity Test: pass Loss on drying: 10.0% max. Sulfated ash(as SO4): 19.5~23.5% |
|
Main Application |
Used as fluorescence indicator. |
1. What are the nicknames of Fluorexon?
Fluorexon is most commonly known as calcein, but it also goes by several other names in scientific literature, including Calcein Blue (though distinct from the actual Calcein Blue dye), Fluorescein Complexon, and Alizarin Complexone. These nicknames reflect its structural similarity to fluorescein and its chelating properties. In some contexts, it may be referred to by its systematic IUPAC name or abbreviated as CAL in biochemical studies. The variety of names arises from its diverse applications in different scientific fields.
2. What is calcein used for?
Calcein is widely used as a fluorescent tracer in biological and medical research. It serves as a marker for cell viability, calcium ion (Ca²⁺) detection, and membrane integrity assays due to its strong green fluorescence. In industrial applications, it helps track water flow and detect leaks. Dentists use calcein-based dyes for plaque disclosure, while biologists employ it to study bone mineralization and osteoblast activity. Its ability to bind metal ions also makes it useful in environmental testing for heavy metal detection.
3. What is the difference between calcein and Calcein-AM?
The key difference lies in their cellular permeability and applications. Calcein is hydrophilic and cannot cross intact cell membranes, making it ideal for labeling damaged cells or extracellular calcium detection. In contrast, Calcein-AM (acetoxymethyl ester) is lipophilic and cell-permeable; once inside cells, esterases cleave the AM group, trapping fluorescent calcein intracellularly. This property makes Calcein-AM superior for live-cell imaging, viability assays, and long-term tracking of intact cells.
4. What is the wavelength of the calcein?
Calcein exhibits peak excitation at 494 nm and emission at 517 nm (green fluorescence), similar to fluorescein but with higher photostability. Its fluorescence is quenched by heavy metals like cobalt or nickel, enabling metal ion detection assays. The wavelength consistency makes it compatible with standard FITC filter sets on microscopes and flow cytometers. When bound to calcium, its fluorescence intensity increases, allowing quantitative Ca²⁺ measurements in biochemical studies.