Produtos Químicos Moneide
Telefone: 86-315-8309571
WhatsApp/WeChat/Celular: 0086-15633399667
Skype: janet-honesta
Correspondência: sales@moneidechem.com
Endereço: 2-7-523 Jidong Building Materials Tangshan, Hebei 064000 China
|
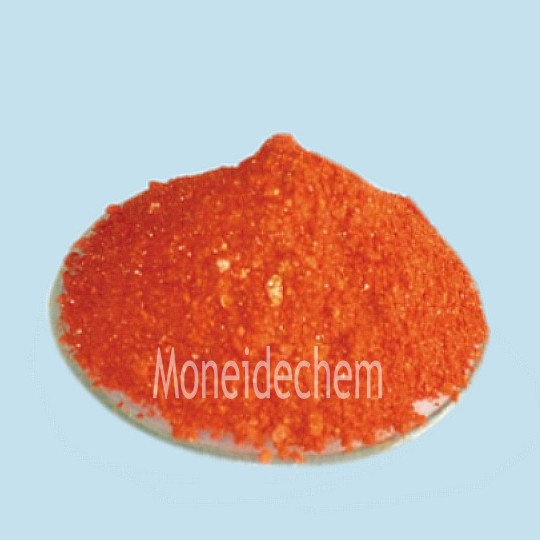
Nome químico |
Methyl orange |
|
Nº CAS. |
547-58-0 |
|
Fórmula molecular |
C14H14N3NaO3S |
|
EINECS No. |
208-925-3 |
|
Peso molecular |
327.33 |
|
Estrutura Molecular |
|
|
Detalhes |
Appearance: Orange yellow or piece crystal PH change range: 3.0(red)~4.4(yellow) Solubility in water: Passes test Sulfated ash: 18.5-22.0% Sensitivity test: Passes test Oxide: Passes test Solubility: easy solve in hot water, water solution is gold yellow, insolve in alcohol. Packing: 25kg/ fibre drum |
|
Aplicação principal |
PH Indicator |
1. What does methyl orange indicate?
Methyl orange is a pH indicator commonly used to detect acidity or alkalinity in chemical titrations, particularly in strong acid-strong base reactions. It changes color within the pH range of 3.1 (red) to 4.4 (yellow), making it ideal for identifying the endpoint in titrations involving hydrochloric acid (HCl) or sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄) with sodium hydroxide (NaOH). Unlike universal indicators, methyl orange is not suitable for weak acid-strong base titrations (e.g., acetic acid with NaOH) because its transition range does not align with their equivalence points.
2. Which colour gives methyl orange?
Methyl orange exhibits distinct color changes based on pH:
Red in strongly acidic conditions (pH ≤ 3.1).
Orange at intermediate pH (~3.1–4.4).
Yellow in weakly acidic to neutral/alkaline solutions (pH ≥ 4.4).
The shift from red to yellow is due to structural changes in the azo group (–N=N–) of the dye, which alters its light absorption properties. This sharp transition makes it a reliable visual marker for titration endpoints.
3. What color is methyl orange at pH 7?
At pH 7 (neutral), methyl orange appears yellow, as its transition to yellow occurs at pH ≥ 4.4 and persists into alkaline conditions. Unlike phenolphthalein (which turns pink in bases), methyl orange remains yellow beyond pH 4.4, making it ineffective for detecting neutral-to-alkaline transitions. Thus, it is primarily used for acidic pH ranges, while alternatives like phenolphthalein are preferred for basic endpoints.
4. Is methyl orange a base or acid?
Methyl orange is an acidic pH indicator itself, but it is neither a base nor an acid in the traditional sense. As an azo dye, it acts as a weak organic compound that undergoes protonation (in acid) or deprotonation (in alkali), causing color changes. Its sulfonate group (–SO₃⁻) makes it water-soluble and reactive to hydrogen ions (H⁺), but it does not participate in acid-base reactions like HCl or NaOH. Instead, it serves as a visual reporter of pH shifts.