Moneide Chemicals
Tel: 86-315-8309571
WhatsApp/WeChat/Mobile: 0086-15633399667
Skype: janet-honest
Mail: sales@moneidechem.com
Address: 2-7-523 Jidong Building Materials Tangshan, Hebei 064000 China
|
Chemical Name |
Acid Green 1 |
|
CAS No. |
19381-50-1 |
|
Molecular formula |
C30H15FeN3Na3O15S3 |
|
EINECS No. |
243-010-2 |
|
Molecular weight |
878.45 |
|
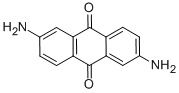
Molecular Structure |
|
|
Details |
Appearance: dark green powder Biological dyeing test: pass |
|
Main Application |
Used as biological dyeing agents. |
1. What is the structure of Acid Green 1?
Acid Green 1, also known as Brilliant Acid Green BS or Wool Green S, is a triarylmethane dye with a complex aromatic structure. Its chemical formula features a central carbon atom bonded to three phenyl groups, one of which carries sulfonate groups for water solubility. The chromophore consists of conjugated double bonds, giving the dye its characteristic green color. The presence of sulfonate groups makes it an acid dye that is suitable for applications requiring binding to positively charged materials like wool and silk.
2. What is Acid Green 1 used for?
Acid Green 1 is primarily used as a textile dye, particularly for protein-based fibers such as wool, silk, and nylon, where it bonds effectively due to its anionic sulfonate groups. It is also employed in biological staining, ink formulations, and paper coloring. In histology, it can be used as a counterstain to highlight specific tissue components. However, its use has declined in some industries due to environmental and health concerns, as synthetic dyes like this can be persistent pollutants if not properly managed.
3. What does Acid Green 1 mean?
Acid Green 1 refers to a synthetic green dye classified under the acid dye category, meaning it contains sulfonic acid groups that make it water-soluble and reactive with cationic substrates. The "1" in its name typically denotes its position in a chemical classification system. As an acid dye, it is used in acidic pH conditions, often in textile dyeing and staining processes. The term distinguishes it from other green dyes, emphasizing its chemical properties and industrial applications, though its usage is now more regulated due to potential toxicity and environmental impact.