Moneide Chemicals
Tel: 86-315-8309571
WhatsApp/WeChat/Mobile: 0086-15633399667
Skype: janet-honest
Mail: sales@moneidechem.com
Address: 2-7-523 Jidong Building Materials Tangshan, Hebei 064000 China
|
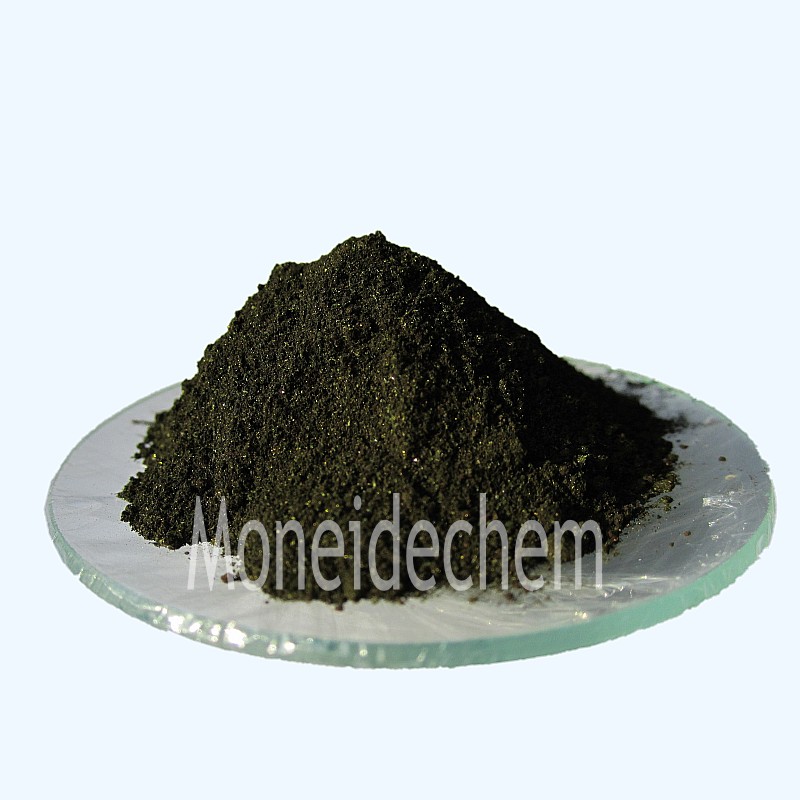
Chemical Name |
Azure II |
|
CAS No. |
|
|
Molecular formula |
C16H18ClN3S.C15H16ClN3S |
|
EINECS No. |
————— |
|
Molecular weight |
625.68 |
|
Molecular Structure |
|
|
Details |
Appearance: Bottle green powder. Biological dyeing test: pass test Ignition residue(SO4): 23.5% max. Package: 25kg/ fibre drum |
|
Main Application |
Used as biological dyeing agents. |
What is Azure 2?
Azure 2 is a synthetic basic dye belonging to the thiazine class, chemically known as 3-Amino-7-dimethylamino-2-methylphenothiazin-5-ium chloride. This blue-green biological stain is widely used in microscopy for chromatin and nucleic acid visualization. Its cationic properties enable strong binding to acidic cellular components, making it valuable for blood smear staining and histological preparations. The dye exhibits metachromatic properties, appearing different colors when bound to various tissue elements. Azure 2 is often combined with other dyes like eosin in Romanowsky-type stains (e.g., Wright-Giemsa) to enhance cellular differentiation in pathological examinations.
Is the Azure 2 a good PC?
Azure 2 is not a personal computer but a biological staining reagent. There appears to be confusion with Microsoft's Azure cloud computing platform. As a histological dye, Azure 2 is considered an excellent staining component for microscopic analysis, particularly in hematology. Its ability to differentiate cellular structures with high contrast makes it valuable for diagnostic pathology. When properly formulated in staining solutions, it produces consistent, reproducible results for blood cell identification and parasite detection in medical laboratories.
Azure II Application
Azure 2's primary application is in medical diagnostics as a component of polychromatic blood stains. It's essential for differential white blood cell counting and malaria parasite identification in peripheral blood smears. The dye also finds use in cytogenetics for chromosome banding studies. Beyond hematology, it stains neural tissues and certain microorganisms in histological sections. Recent applications include flow cytometry and immunocytochemistry where it serves as a counterstain to highlight nuclei. Its metachromatic properties are exploited in special stains for mast cells and cartilage components in connective tissue studies.