Welina mai iā Tangshan Moneide Trading Co., Ltd.
Nā Mea Kimi Moneide
Tel: 86-315-8309571
WhatsApp/WeChat/Mobile: 0086-15633399667
Skype: janet-honest
Leka: sales@moneidechem.com
Wahi: 2-7-523 Jidong Building Materials Tangshan, Hebei 064000 Kina
|
Inoa Kimia |
Methyl red |
|
CAS No. |
493-52-7 |
|
ʻAno molekala |
C15H15N3O2 |
|
EINECS No. |
207-776-1 |
|
Kaumaha molekula |
269.30 |
|
Hoʻokumu Molecular |
|
|
Nā kikoʻī |
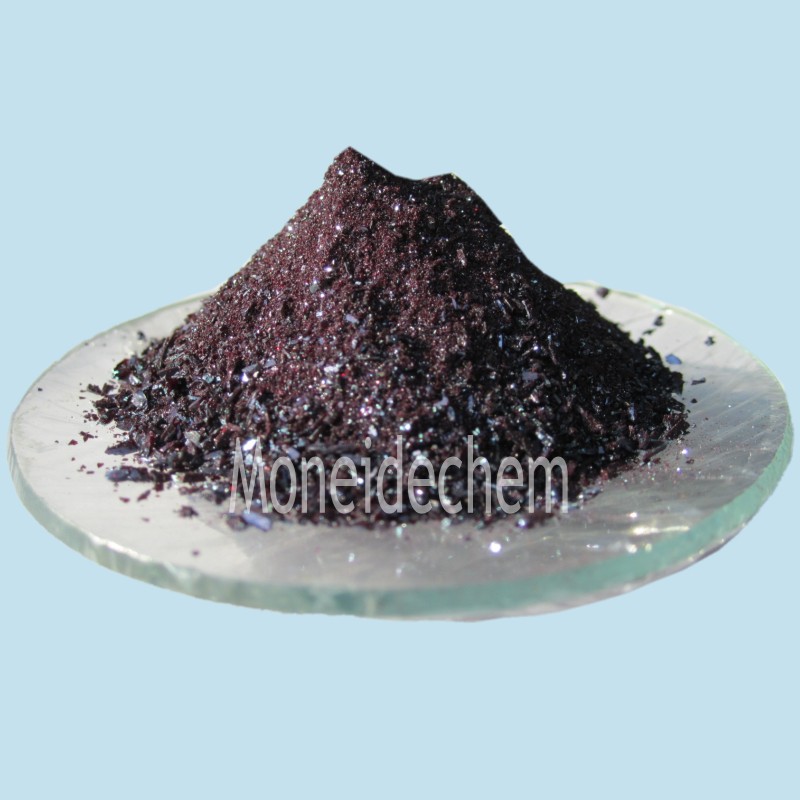
Appearance: With shine violet crystalor carmine powder Max Absorption wavelength, λ1(PH4.5): 523~528 nm Max Absorption wavelength, λ2(PH6.2): 427~437 nm Mass absorption coefficient , λ1 (PH4.5):130 L/(cm·g) min Mass absorption coefficient , λ2 (PH6.2):70 L/(cm·g) min PH discoloration range:4.5(Red)-6.2(Yellow) Solubility in Ethanol: Pass Loss on drying: 1.0 % max Residue on ignition (sulfate):0.2%max Melting point: 181-182℃ Solubility: solve in alcohol, insolve in water. Packing: 25kg/ fibre drum |
|
Noi Nui |
PH Indicator |
What is methyl red used for?
Methyl red is a pH indicator widely used in chemistry and microbiology to detect acidity changes. In laboratories, it helps monitor pH shifts in solutions, turning red below pH 4.4 and yellow above pH 6.2. A key application is in the Methyl Red (MR) test, part of the IMViC series, which identifies enteric bacteria like E. coli based on their ability to produce stable acidic end products from glucose fermentation. Additionally, methyl red is used in titrations, environmental testing, and educational demonstrations to visually illustrate pH transitions in chemical reactions.
Why does methyl red turn pink?
Methyl red turns pink (or red) in acidic conditions (pH ≤ 4.4) due to a structural change in its azo dye molecule. In low pH environments, the dye gains hydrogen ions (protonation), shifting its molecular conformation and altering its light absorption properties. This causes it to reflect red wavelengths. As pH rises (≥6.2), it loses protons, turning yellow. The reversible color change makes methyl red a reliable indicator for detecting acidity in biochemical assays, bacterial cultures, and chemical experiments.
What function does methyl red play in the experiment?
In experiments, methyl red primarily serves as a visual pH indicator, helping researchers track acidity changes. In microbiology, it distinguishes bacteria that produce mixed acids during fermentation (e.g., E. coli turns the medium red) from those that do not (e.g., Enterobacter remains yellow). In chemistry, it aids in titrations by signaling endpoint transitions. Its vivid color shift provides immediate feedback, ensuring accurate pH monitoring without requiring advanced instrumentation, making it a cost-effective tool in both educational and professional lab settings.