Welina mai iā Tangshan Moneide Trading Co., Ltd.
Nā Mea Kimi Moneide
Tel: 86-315-8309571
WhatsApp/WeChat/Mobile: 0086-15633399667
Skype: janet-honest
Leka: sales@moneidechem.com
Wahi: 2-7-523 Jidong Building Materials Tangshan, Hebei 064000 Kina
Basic Red 2
|
Inoa Kimia |
Basic Red 2 |
|
Nā huaʻōlelo like |
C.I. 50240; Safranine O; Safranine T; 3,7-Diamino-2,8-dimethyl-5-phenylphenazinium chloride |
|
CAS No. |
477-73-6 |
|
ʻAno molekala |
C20H19ClN4 |
|
EINECS No. |
207-518-8 |
|
Kaumaha molekula |
350.85 |
|
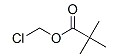
Hoʻokumu Molecular |
|
|
Nā kikoʻī |
Appearance: brownish red powder Biological dyeing test: pass |
|
Noi Nui |
Used as biological stain. |
What is the Basic Red 2 dye?
Basic Red 2 is a synthetic cationic dye belonging to the azine class of dyes, chemically known as Safranin O. Its molecular structure features a phenazine core with dimethylamino substituents, giving it a distinctive red color and positive charge that enables strong binding to negatively charged substrates. The dye typically appears as dark red crystals or powder that dissolves readily in water and alcohol to produce an intense reddish-pink solution. As a basic dye, it carries permanent positive charges on its chromophore, making it particularly effective for staining biological specimens and textile fibers. Its chemical stability and vibrant coloration have made it a standard in both industrial and laboratory applications for over a century.
What is Basic Red 2 used for?
Basic Red 2 has diverse applications across multiple fields, most notably as a biological stain in histology and microbiology. It's commonly used in Gram staining procedures as a counterstain to differentiate bacterial types, and in botanical studies to highlight lignified tissues. The textile industry employs it for dyeing silk, wool, and modified acrylic fibers, where it produces bright reddish hues with good lightfastness. Additionally, it serves as a redox indicator in analytical chemistry and finds use in paper coloration, ink formulations, and leather staining. Recent applications include its use as a photosensitizer in solar cells and as a fluorescent marker in certain biochemical assays, demonstrating its continued relevance in modern technologies.
What is another name for Basic Red 2?
Basic Red 2 is more widely known in scientific literature as Safranin O or Safranin T, names derived from its similarity to the natural saffron dye. In chemical nomenclature, it may be referred to as 3,7-diamino-2,8-dimethyl-5-phenylphenazinium chloride. The Color Index identifies it as CI 50240, while industrial applications sometimes use trade names like Cotton Red or Gossypimine. These various names reflect its long history of use across different disciplines since its first synthesis in the 19th century. The "O" designation in Safranin O distinguishes it from similar safranin compounds with slightly different methylation patterns that exhibit distinct staining properties.