Welina mai iā Tangshan Moneide Trading Co., Ltd.
Nā Mea Kimi Moneide
Tel: 86-315-8309571
WhatsApp/WeChat/Mobile: 0086-15633399667
Skype: janet-honest
Leka: sales@moneidechem.com
Wahi: 2-7-523 Jidong Building Materials Tangshan, Hebei 064000 Kina
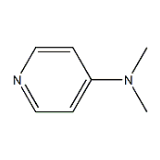
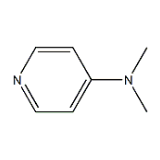
4-Dimethylamino Pyridine
|
Inoa Kimia |
4-Dimethylamino pyridine |
|
Nā huaʻōlelo like |
N,N-Dimethylpyridin-4-amine; DMAP |
|
CAS No. |
1122-58-3 |
|
ʻAno molekala |
C7H10N2 |
|
Kaumaha molekula |
122.17 |
|
Hoʻokumu Molecular |
|
|
Nā kikoʻī |
Appearance: off-white to white crystal Purity: 99.0% min. |
|
Noi Nui |
It is mainly used for the super nucleophilic acylation catalyst.
|
- Esterification Reactions: DMAP is widely used in esterification reactions, especially those involving anhydrides. For example, in the synthesis of esters from acetic anhydrides and alcohols, DMAP acts as a catalyst to accelerate the reaction. The reaction mechanism involves the formation of an ion pair between DMAP and the anhydride, followed by the addition of the alcohol and subsequent elimination steps to form the ester. This process allows for the synthesis of esters under milder reaction conditions and with higher yields compared to traditional methods.
- Acylation Reactions: It is a key catalyst in various acylation reactions. In the acylation of amines and alcohols with acyl chlorides or anhydrides, DMAP enhances the reactivity of the substrates. This is particularly useful in the synthesis of pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and fine chemicals, where precise control over the acylation process is crucial for obtaining the desired products with specific functional groups and properties.
- Cyclization and Rearrangement Reactions: DMAP can also catalyze cyclization and rearrangement reactions. For instance, in the Staudinger synthesis of β - lactams, DMAP plays a vital role in promoting the reaction pathway that leads to the formation of the characteristic β - lactam ring structure. These types of reactions are important in the synthesis of bioactive compounds and natural products.
- Intermediate in Drug Synthesis: In the pharmaceutical industry, 4 - Dimethylamino Pyridine is often used as an intermediate in the synthesis of various drugs. It participates in reactions that build the complex molecular structures required for pharmaceutical compounds. For example, in the synthesis of certain anti - inflammatory drugs or antiviral agents, DMAP - catalyzed reactions are used to introduce specific functional groups or to form key chemical bonds, contributing to the overall structure and activity of the drug molecule.
- Process Optimization: The use of DMAP in pharmaceutical manufacturing processes can optimize reaction conditions, reduce reaction times, and improve product purity. This not only increases the efficiency of drug production but also helps in meeting the strict quality control requirements of the pharmaceutical industry.
- Polymerization Catalyst: In polymer science, DMAP can be used as a catalyst in certain polymerization reactions. It can influence the polymerization process by promoting the reaction between monomers, controlling the molecular weight and structure of the resulting polymers. This is useful in the production of polymers with specific properties, such as those used in coatings, adhesives, and high - performance materials.
- Surface Modification: DMAP can be employed for surface modification of materials. By reacting with the surface of polymers or other materials, it can introduce functional groups, which can enhance properties such as adhesion, wettability, or chemical resistance. This surface modification is valuable in applications where materials need to interact with specific environments or other substances.
- 4 - Dimethylamino Pyridine is considered harmful if swallowed, inhaled, or absorbed through the skin.
- It is corrosive and can cause severe skin burns and eye damage. Prolonged or repeated exposure may have adverse effects on health.
- Contact with strong oxidizing agents or acids can lead to dangerous reactions.
- When handling DMAP, always wear appropriate personal protective equipment, including chemical - resistant gloves, safety goggles with side - shields, and a lab coat or protective apron.
- Work in a well - ventilated area, preferably under a fume hood, to avoid inhalation of dust or vapors.
- In case of contact with skin, immediately remove contaminated clothing and rinse the affected area with plenty of water for at least 15 minutes. Seek medical attention promptly. If the compound gets into the eyes, rinse the eyes with copious amounts of water for at least 15 minutes, lifting the eyelids occasionally, and then seek immediate medical help.
- Do not eat, drink, or smoke in the area where 4 - Dimethylamino Pyridine is being used.
- Store the product in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight and heat sources.
- Keep it in a tightly sealed container to prevent moisture absorption and contact with air, which could potentially affect its chemical properties.
- Store it separately from incompatible substances such as strong acids, oxidizing agents, and other reactive chemicals to avoid dangerous reactions.