Welcome to Tangshan Moneide Trading Co., Ltd.
Moneide Chemicals
Tel: 86-315-8309571
WhatsApp/WeChat/Mobile: 0086-15633399667
Skype: janet-honest
Mail: sales@moneidechem.com
Address: 2-7-523 Jidong Building Materials Tangshan, Hebei 064000 China
|
Chemical Name |
Аллилтиомочевина |
|
Synonyms |
Thiosinamine |
|
CAS No. |
109-57-9 |
|
EINECS No. |
203-683-5 |
|
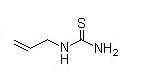
Molecular formula |
C4H8N2S |
|
Molecular weight |
116.18 |
|
Molecular Structure |
|
|
Details |
Appearance:white crystal Assay: 98%min Melting point: 76-78.5℃ Ignition residue: 0.008MEQ/G max Moisture: 0.1%max Packing: 25KG/ fibre drum |
|
Main Application |
Used as cyanide-free copper plating additives, preservatives, also used in organic synthesis. |
Allylthiourea is an organosulfur compound that combines a thiourea group (-CSNH₂) with an allyl group (CH₂=CH–CH₂-), giving it strong chelating, reducing, and biological activity. This makes it useful in various chemical, industrial, and research applications.
1. Heavy Metal Chelating Agent
Allylthiourea is commonly used as a chelating agent for metal ions, particularly in wastewater treatment and analytical chemistry, where it helps in the removal or detection of trace metals like mercury, copper, and lead through complexation.
2. Corrosion Inhibition
Due to its ability to form stable complexes with metal surfaces, allylthiourea serves as a corrosion inhibitor in industrial systems, such as boilers, pipelines, and cooling towers, where it protects metals from oxidative damage.
3. Biochemical Research
In microbiology and enzymology, allylthiourea is used to inhibit certain enzyme activities, such as urease, making it useful in metabolic studies and the control of nitrification in soil or wastewater research.
4. Electroplating Additive
Allylthiourea may be used as an additive in electroplating baths, especially in nickel and copper plating, where it acts as a grain refiner or brightener to improve deposit smoothness and appearance.
5. Intermediate in Organic Synthesis
With its reactive thiourea and allyl groups, it is also used as an intermediate in the synthesis of pharmaceuticals and fine chemicals, offering structural versatility for further modification in drug development or agrochemical production.