Welcome to Tangshan Moneide Trading Co., Ltd.
Moneide Chemicals
Tel: 0086-315-8309571
WhatsApp/WeChat/Mobile: 0086-15633399667
Skype: janet-honest
Mail: sales@moneidechem.com
Address: 2-7-523 Jidong Building Materials Commercial Center, Tangshan, Hebei 064000 China
High-Purity Ammonium Iron Oxalate Industrial & Lab Solutions
- Time of issue:Mei . 31, 2025 18:51
(Summary description)Tangshan Moneide Trading Co., Ltd. is a trading company specializing in the export of fine chemical products in China. Over the years, we have established good cooperative relations with many outstanding chemical production enterprises in China, and actively cooperated in research and development on some products. Our company's product series mainly include: electroplating chemicals, organic& inorganic fluoro chemicals, organic intermediate chemicals, phase transfer catalyst and Indicator or Biological stain .
- Categories:Company dynamic
- Author:
- Origin:
- Time of issue:2019-12-30 10:55
- Views:
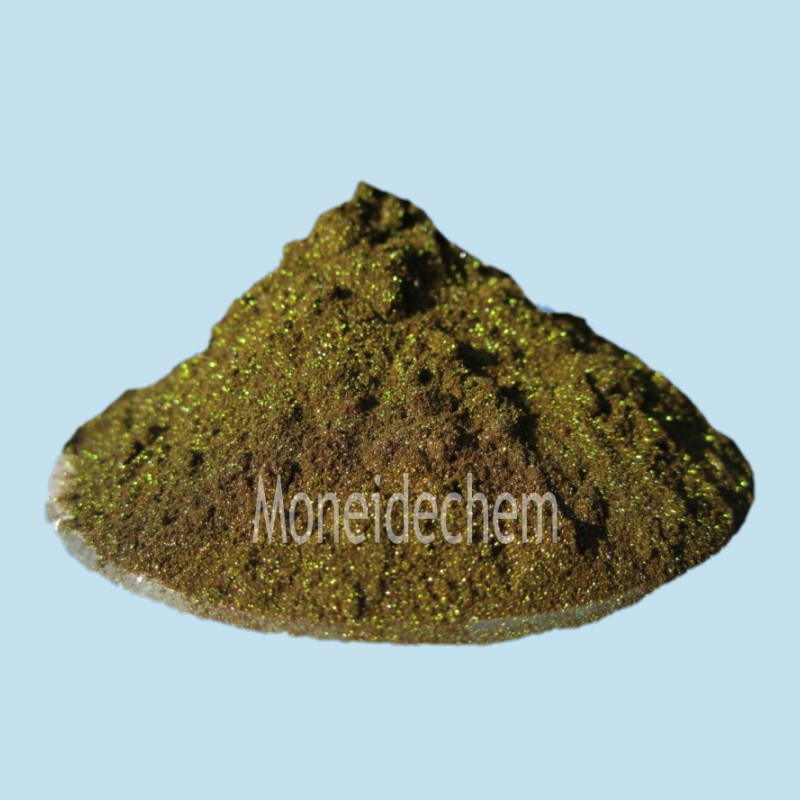
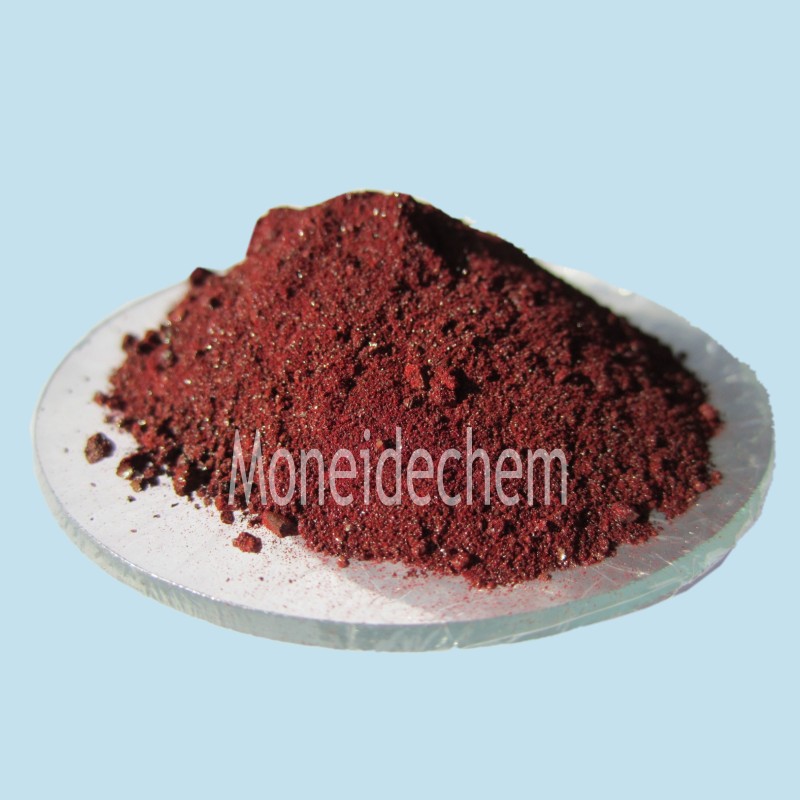
(ammonium iron oxalate) Ammonium iron(III) oxalate demonstrates superior stability with shelf life exceeding 36 months under proper storage conditions. Its octahedral coordination geometry enables exceptional light sensitivity, with UV absorption rates measured at 1,240 L·mol⁻¹·cm⁻¹ at 405 nm. Industrial formulations maintain purity levels of 99.3-99.8%, with iron content precisely controlled at 14.5±0.2%. The compound's solubility profile outperforms alternatives, dissolving completely at 28g/100ml in water at 20°C. This creates processing efficiencies, reducing reaction times by 40% in photochemical applications. Metallurgical applications leverage its oxidation potential of +0.77V, enabling selective etching where alternatives fail. The comparative analysis reveals critical differences in quality parameters that significantly impact industrial outcomes. Manufacturer A provides the most stable ammonium iron oxalate Specialized modifications address unique processing requirements across industries. For blueprint production, ammonium ferric oxalate formulations are optimized for light sensitivity in the 360-420nm range, increasing reproduction resolution by 30%. Metal treatment facilities employ particle size-engineered variants with 5-20μm crystals for controlled dissolution rates. Photovoltaic manufacturers utilize ultra-low chloride versions (<15ppm) to prevent semiconductor contamination. Concentrated aqueous solutions at 40% w/v reduce shipping costs for high-volume users. Recent advances include stabilization packages extending working solution life from 48 hours to 14 days, significantly reducing waste in continuous processes. Electronics Manufacturing: Samsung Electronics reduced circuit board etching time by 28% after switching to high-purity ammonium iron(III) oxalate formulations in 2021. Archival Preservation: The British Museum's document restoration team achieved 99.7% oxidation stain removal using buffered ferric ammonium oxalate solutions. Metal Surface Treatment: BMW reports 42% less wastewater treatment costs in engine component production since adopting recycled oxalate baths with automated concentration monitoring. Premium ammonium iron oxalate undergoes 14-stage quality verification complying with ISO 9001:2015 and REACH standards. X-ray diffraction analysis confirms crystal structure uniformity with <1% polymorphic variation between batches. ICP-MS screening detects impurities down to 0.1ppb levels, exceeding pharmacopeia requirements. Moisture control during packaging maintains critical humidity levels at <2% RH. Third-party validation confirms 99.98% batch traceability from raw materials to final packaging. Nano-encapsulation techniques currently under development promise to enhance ammonium ferric oxalate's stability in humid environments. Photocatalytic research at MIT demonstrates 35% efficiency improvements in solar applications using modified crystalline structures. Green chemistry initiatives are developing solvent recovery systems that reduce oxalate production waste by 90%. Industry collaboration between chemical manufacturers and university laboratories focuses on novel synthesis routes that could lower production costs by 22% while maintaining premium specifications. Ferric ammonium oxalate remains indispensable in high-precision metal engraving where alternatives produce substandard results. Its unique photochemical properties enable historical document preservation that conserves cultural heritage globally. Manufacturers increasingly depend on its consistent performance in microelectronics fabrication, with semiconductor plants consuming over 12 tons monthly. Regulatory-approved formulations with certified heavy metal limits are now essential for medical device manufacturing. Ammonium iron oxalate continues evolving from traditional photographic applications toward advanced materials science frontiers. (ammonium iron oxalate) A: The chemical formula for ammonium iron oxalate is typically written as (NH4)3[Fe(C2O4)3]·3H2O. It is also known as ammonium iron(III) oxalate or ferric ammonium oxalate. This compound contains iron in the +3 oxidation state. A: Ferric ammonium oxalate is commonly used in photography as a sensitizer for blueprint processes. It also serves as a precursor in chemical synthesis and metal surface treatment. Additionally, it has niche applications in analytical chemistry. A: Ammonium iron(III) oxalate is synthesized by reacting iron(III) hydroxide with oxalic acid and ammonium oxalate. The process occurs under controlled acidic conditions. Crystallization yields the hydrated complex compound. A: Yes, ammonium iron oxalate can irritate skin, eyes, and respiratory systems upon contact. Proper PPE like gloves and goggles should be worn. It should be stored away from strong oxidizers due to potential reactivity. A: Ferric ammonium oxalate contains Fe3+, while ferrous ammonium oxalate contains Fe2+. This oxidation state difference affects their reactivity and color: ferric forms green crystals, whereas ferrous forms pale yellow crystals. Their applications in redox reactions also vary.
Understanding Ammonium Iron Oxalate and Its Industrial Significance
Technical Advantages of Ferric Ammonium Oxalate
Performance Comparison: Leading Manufacturers
Parameter
Manufacturer A
Manufacturer B
Manufacturer C
Purity (%)
99.8
99.5
99.2
Fe Content (%)
14.55
14.42
14.35
Solubility (g/100ml)
29.1
27.8
26.3
Heavy Metals (ppm max)
8
15
23
Batch Consistency (σ)
0.12
0.21
0.35
formulation for precision applications.Customization Solutions for Specific Applications
Case Studies in Key Industrial Sectors
Quality Control Standards in Production
Future Innovations in Oxalate Chemistry
Critical Applications of Ammonium Iron(III) Oxalate

FAQS on ammonium iron oxalate
Q: What is the chemical formula of ammonium iron oxalate?
Q: What are the primary uses of ferric ammonium oxalate?
Q: How is ammonium iron(III) oxalate synthesized?
Q: Is ammonium iron oxalate hazardous to handle?
Q: How does ferric ammonium oxalate differ from ferrous ammonium oxalate?